Summary: in this tutorial, we will show you how to delete data from multiple tables by using MySQL DELETE JOIN statement.
In the previous tutorial, you learned how to delete rows of multiple tables by using:
- A single
DELETEstatement on multiple tables. - A single
DELETEstatement on multiple related tables which the child table have anON DELETE CASCADEreferential action for the foreign key.
This tutorial introduces to you a more flexible way to delete data from multiple tables using
INNER JOINor LEFT JOIN clause with the DELETE statement.
MySQL DELETE JOIN with INNER JOIN
MySQL also allows you to use the
INNER JOIN clause in the DELETE statement to delete rows from a table and the matching rows in another table.
For example, to delete rows from both
T1 and T2 tables that meet a specified condition, you use the following statement:
Notice that you put table names
T1 and T2 between the DELETE and FROM keywords. If you omit T1 table, the DELETE statement only deletes rows in T2 table. Similarly, if you omitT2 table, the DELETE statement will delete only rows in T1 table.
The expression
T1.key = T2.key specifies the condition for matching rows between T1 andT2 tables that will be deleted.
The condition in the
WHERE clause determine rows in the T1 and T2 that will be deleted.
MySQL DELETE JOIN with INNER JOIN example
Suppose, we have two tables
t1 and t2 with the following structures and data:
The following statement deletes the row with id 1 in the
t1 table and also row with ref 1 in the t2 table using DELETE...INNER JOIN statement:
The statement returned the following message:
It indicated that two rows have been deleted.
MySQL DELETE JOIN with LEFT JOIN
We often use the
LEFT JOIN clause in the SELECT statement to find rows in the left table that have or don’t have matching rows in the right table.
We can also use the
LEFT JOIN clause in the DELETE statement to delete rows in a table (left table) that does not have matching rows in another table (right table).
The following syntax illustrates how to use
DELETE statement with LEFT JOIN clause to delete rows from T1 table that does not have corresponding rows in the T2 table:
Note that we only put
T1 table after the DELETE keyword, not both T1 and T2 tables like we did with the INNER JOIN clause.MySQL DELETE JOIN with LEFT JOIN example
See the following
customers and orders tables in the sample database: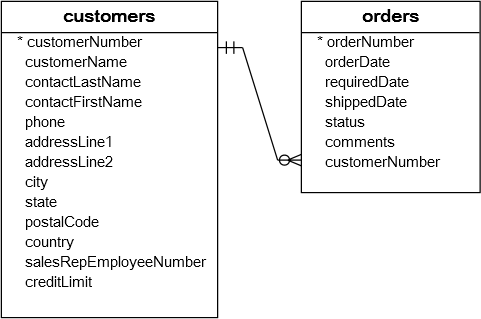
Each customer has zero or more orders. However, each order belongs to one and only one customer.
We can use
DELETE statement with LEFT JOIN clause to clean up our customers master data. The following statement removes customers who have not placed any order:
We can verify the delete by finding whether customers who do not have any order exists using the following query:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
SELECT
c.customerNumber,
c.customerName,
orderNumber
FROM
customers c
LEFT JOIN
orders o ON c.customerNumber = o.customerNumber
WHERE
orderNumber IS NULL;
|
The query returned an empty result set which is what we expected.
In this tutorial, you have learned how to use the MySQL
DELETE JOIN statement to delete data from two or more tables.